树
1 树的概念
树 是一种数据结构,它是由n(n>=1)个有限点组成一个具有层次关系的集合,形状根朝上,叶朝下,像一颗倒挂的树。每个结点有零或者多个子结点,每一个子结点可以分为多个不相交的子树。 树的一些定义: * 空集合也是树,称为空树,空树中没有结点。 * 一个结点含有的子树的根结点称为该结点的子结点 * 结点的度是一个结点含有的子结点的个数 * 度为0的结点称为叶结点 * 度不为0的结点称为非终端结点或者分支结点 * 树的度:一颗树中,最大的结点的度称为树的度 * 结点的层次:从根开始,根为第一层,根的子结点为第二层,以此类推 * 树的高度或深度:树中结点的最大层次 * 森林:由m(m>=0)颗互不相交的树的集合称为森林
树的种类: * 无序树: 树中任意结点的子结点之间没有顺序关系,也称为自由树 * 有序树: 树中任意结点的子结点之间有顺序关系 * 二叉树: 每个结点最多包含有两个子树的树称为二叉树 * 满二叉树: 叶结点除外的所有结点均含有两个子树 * 完全二叉树: 有2^k-1个结点的满二叉树 * 哈夫曼树: 带权路径最短的二叉树称为哈夫曼树或者最优二叉树 一般树的图示如下图所示: 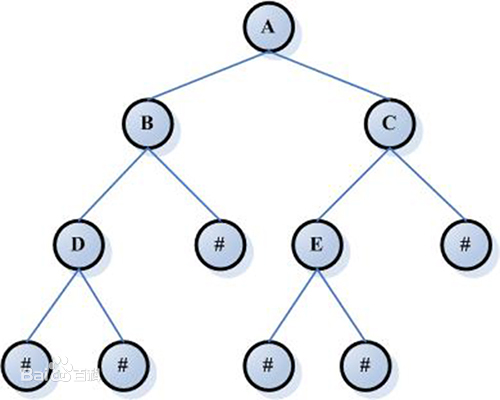
2 树的遍历和查找
树的遍历方法有三种: * 前序遍历: 根结点->遍历左子树->遍历右子树 * 中序遍历: 遍历左子树->根结点->遍历右子树 * 后序遍历: 遍历左子树->遍历右子树->根结点
树的查找也有三种方法: * 前序查找: 根结点-> 遍历左子树 -> 遍历右子树 * 中序查找: 遍历左子树 -> 根结点 -> 遍历右子树 * 后序查找: 遍历左结点 -> 遍历右结点 -> 根结点
3树结点的删除
这里创建的树是单向的,所以要判断当前的子结点是否需要删除结点,而不能判断当前这个结点是否需要删除。 * 1 如果当前结点的左子结点不为空,并且左子结点就是要删除结点,就将this.left = null,返回。 * 2 如果当前结点的右子结点不为空,并且右子结点就是要删除的结点,就将this.right=null,并且返回。 * 3 上述两步均没能删除的话,就向左子树递归删除 * 4 上述三步均没有删除的话,向右子树递归删除
代码实现: 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310package BinaryTree;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
*
* @Auther: ChrisPeng
* @Date: 2021/01/11/16:00
* @Description: 树的创建和各种功能
*/
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//先创建一颗二叉树
BinaryTree binaryTree = new BinaryTree();
//创建需要的节点
HeroNode root = new HeroNode(1, "宋江");
HeroNode node2 = new HeroNode(2, "吴用");
HeroNode node3 = new HeroNode(3, "卢俊义");
HeroNode node4 = new HeroNode(4, "林冲");
//手动创建二叉树
binaryTree.setRoot(root);
root.setLeft(node2);
root.setRight(node3);
node3.setRight(node4);
//测试
System.out.println("前序遍历");
binaryTree.postOrder();
System.out.println("中序遍历");
binaryTree.infixOrder();
System.out.println("后序遍历");
binaryTree.postOrder();
HeroNode heroNode = binaryTree.preOrderSearch(3);
if (heroNode != null){
System.out.printf("no = %d name = %s",heroNode.getNo(),heroNode.getName());
}else {
System.out.println("查无此人");
}
//删除节点
System.out.println("删除前");
binaryTree.preOrder();
binaryTree.delNode(4);
System.out.println("删除后");
binaryTree.postOrder();
}
}
//定义二叉树
class BinaryTree{
private HeroNode root;
public void setRoot(HeroNode root) {
this.root = root;
}
//删除节点
public void delNode(int no){
if (root != null){
//判断是否为要删除的结点
if (root.getNo() == no){
root = null;
}else {
root.delNode(no);
}
}else {
System.out.println("空树无法删除");
}
}
//前序遍历
public void preOrder(){
if (this.root != null){
this.root.preOrder();
}else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
//中序遍历
public void infixOrder(){
if (this.root != null){
this.root.infixOrder();
}else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
//后序遍历
public void postOrder(){
if (this.root != null){
this.root.postOrder();
}else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
//前序查找
public HeroNode preOrderSearch(int no){
if (root != null){
return root.postOrderSearch(no);
}else {
return null;
}
}
public HeroNode infixOrderSearch(int no){
if (root != null){
return root.infixOrderSearch(no);
}else {
return null;
}
}
//后序查找
public HeroNode postOrderSearch(int no){
if (root != null){
return this.root.postOrderSearch(no);
}else {
return null;
}
}
}
//先创建heronode节点
class HeroNode{
private int no;
private String name;
private HeroNode left;//默认null
private HeroNode right;//默认null
public HeroNode(int no,String name){
this.no = no;
this.name = name;
}
public int getNo() {
return no;
}
public void setNo(int no) {
this.no = no;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public HeroNode getLeft() {
return left;
}
public void setLeft(HeroNode left) {
this.left = left;
}
public HeroNode getRight() {
return right;
}
public void setRight(HeroNode right) {
this.right = right;
}
public String toString() {
return "HeroNode{" +
"no=" + no +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
//递归删除结点
//如果删除的是叶子结点,则删除该结点
//如果删除的结点是非叶子结点,则删除该子树
public void delNode(int no){
/**
* 当前创建的二叉树是单向的,所以判断当前的子结点是否需要删除节点,而不能判断当前这个节点是否需要删除
*
*/
//如果当前节点的左子节点不为空,并且左子节点就是要删除节点
//就将this.left=null,并且返回
if (this.left != null && this.left.no == no){
this.left = null;
return;
}
//如果当前结点的右子结点不为空,并且右子结点就是要删除节点
//就将this.right =null, 并且返回
if (this.right != null && this.right.no == no){
this.right = null;
return;
}
//上述两步没有删除的话就向左子树递归删除
if (this.left != null){
this.left.delNode(no);
}
//上述三步都没有删除的话,向右子树递归删除
if (this.right != null){
this.right.delNode(no);
}
}
//编写前序遍历的方法
public void preOrder(){
System.out.println(this);//先输出父节点
//递归向左子树前序遍历
if (this.left != null){
this.left.preOrder();
}
//递归向右子树前序遍历
if (this.right != null){
this.right.preOrder();
}
}
//中序遍历
public void infixOrder(){
//递归向左子树中序遍历
if (this.left != null){
this.left.infixOrder();
}
//输出父节点
System.out.println(this);
//向右子树中序遍历
if (this.right != null){
this.right.infixOrder();
}
}
//后序遍历
public void postOrder(){
if (this.left != null){
this.left.postOrder();
}
if (this.right != null){
this.right.postOrder();
}
System.out.println(this);
}
//前序遍历查找
/**
*
* @param no 查找的no
* @return 如果找到就返回该NODE,没有的话返回null
*/
public HeroNode preOrderSearch(int no){
//比较当前节点是不是
if (this.no == no){
return this;
}
//判断当前节点的左子节点是否为空,如果不是,则递归前序查找
//当前的节点的右子节点是否为空,如果不是,继续向右递归前序查找
HeroNode resNode = null;
if (this.left != null){
resNode = this.left.preOrderSearch(no);
}
if (resNode != null){
//左子树找到
return resNode;
}
//左递归前序查找,找到节点,则返回,否则继续判断
//当前的节点的右子节点是否为空,如果不是,则继续向右递归前序查找
if (this.right != null){
resNode = this.right.preOrderSearch(no);
}
return resNode;
}
//中序遍历查找
public HeroNode infixOrderSearch(int no){
//判断当前节点的左子节点是否为空,如果不是空,则递归中序查找
HeroNode resNode = null;
if (this.left != null){
resNode = this.left.infixOrderSearch(no);
}
if (resNode != null){
return resNode;
}
//如果找到,则返回,如果没有找到,,就和当前节点比较,如果是则返回
if (this.no == no){
return this;
}
//否则继续进行右递归的中序查找
if (this.right != null){
resNode = this.right.infixOrderSearch(no);
}
return resNode;
}
//后序遍历查找
public HeroNode postOrderSearch(int no){
//判断当前节点的左子节点是否为空,如果不是空,则递归后序查找
HeroNode resNode = null;
if (this.left != null){
resNode = this.left.postOrderSearch(no);
}
if (resNode != null){//说明在左子树找到
return resNode;
}
//如果左子树没有找到,则向右子树递归进行后序查找
if (this.right != null){
resNode = this.right.postOrderSearch(no);
}
if (resNode != null){
return resNode;
}
//如果左右子树都没有找到,那么说明当前节点不是
if (this.no == no){
return this;
}
return resNode;
}
}
4. 二叉树前中后序遍历迭代实现
递归的实现就是:每一次调用递归都会把函数的局部变量、参数值和返回地址等压入调用栈中,然后递归返回的时候,从栈顶弹出上一次递归的各项参数,所以这就是为啥递归可以返回上一层的位置。
前序遍历
前序遍历是左中右的次序,每次先处理的是中间节点,先将根节点放入到栈中,然后将右子节点加入栈中,再加入左子节点。
1 | class Solution{ |
中序遍历
前序遍历的代码其实是不能直接套用在中序遍历上的,因为前序遍历的顺序是中左右,要处理的元素也是中间节点,要访问的元素和要处理的元素顺序是一致的,都是中间节点。
中序遍历是左中右,先访问的是二叉树顶部的节点,然后一层一层向下访问,直到树左面的最底部,再开始处理节点,这就导致了处理顺序和访问顺序是不一致的。
那么在使用迭代法写中序遍历,就需要借用指针的遍历来帮助访问节点,栈则用来处理节点上的元素。
1 | class Solution{ |
后序遍历
后序遍历的顺序是左右中,那么只需要反转前序遍历得到的结果
1 | class Solution { |
5. 二叉树的层序遍历
二叉树的另一种遍历的方式就是从上到下一层一层的去遍历二叉树。这个需要借助一个辅助数据结构队列来实现,队列先进先出,符合一层一层遍历的逻辑。
1 | class Solution { |
6. 判断树是否为对称二叉树
要判断一棵树是不是对称二叉树,需要比较的是当前节点的两个子树的里侧和外侧的元素是否相等。可以考虑对于一层来说,左子节点的左子节点和右子节点的右子节点值相等,左子节点的右子树和右子节点的左子树相等,这样的话才是满足对称的要求。
1 | class Solution { |
当然这种问题也可以使用迭代的方法来求解:
(1)使用队列:
1 | class Solution { |
(2)使用栈:(只是进出的顺序不一致,注意这个就好了)
1 | class Solution { |
7. 计算二叉树的所有路径
要求统计从根节点到叶子节点的路径,所以需要前序遍历,这样才方便让父节点指向子节点。这里需要用到回溯来回退一个路径再进入另一个路径。
用递归的思想来写的话就是以下几个步骤:
递归函数,参数以及返回值
要传入根节点,记录每条路径的path,和存放结果集的result,递归不需要返回值
1
private void traversal(TreeNode root, List<Integer> paths, List<String> res)
确定递归终止条件
本题的终止条件是找到了叶子节点就截止,也就是当cur不为空,其左右孩子都为空的时候就找到了叶子节点。
1
if (root.left == null && root.right == null)
确定单层递归逻辑
因为是前序遍历,所以要先处理中间节点,先放进path中,然后是递归和回溯的过程,递归时当cur空的时候就不进行下一层的递归了,所以递归要加上判断语句。这时候还得考虑回溯的问题,path不能一直加节点,还需要删节点,然后才能加入新的节点。那要如何回溯?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8if (root.left != null) {
traversal(root.left, paths, res);
paths.remove(paths.size() - 1);// 回溯
}
if (root.right != null) {
traversal(root.right, paths, res);
paths.remove(paths.size() - 1);// 回溯
}
总共的代码如下所示:
1 | class Solution { |
